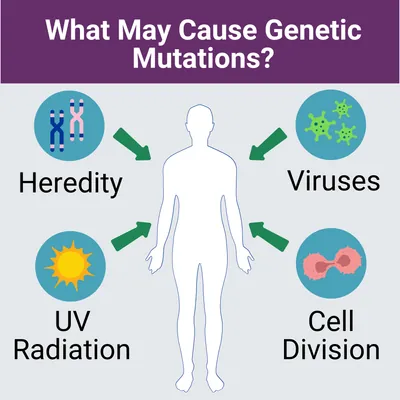
Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy is caused by genetic mutations, also known as pathogenic variants. Genetic mutations can be hereditary, when parents pass them down to their children, or they may occur randomly when cells are dividing. Genetic mutations may also result from contracted viruses, environmental factors, such as UV radiation from sunlight exposure, or a combination of any of these.
Learn more about genetic diseases from the National Library of Medicine (NLM).If you suspect you may have this disease, you may want to start collecting your family health history. Information such as other family members who have had similar symptoms, when their/your symptoms first appeared, or exposures to any potential disease-causing environmental factors should be discussed with your medical team.
This tool from the Surgeon General can help you collect your family health history.