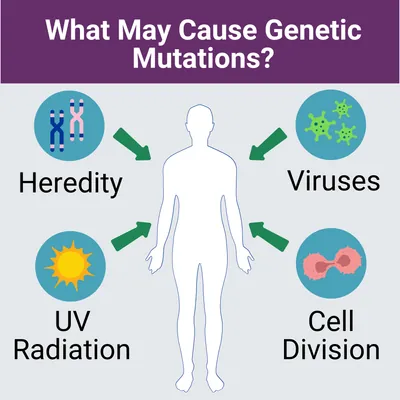
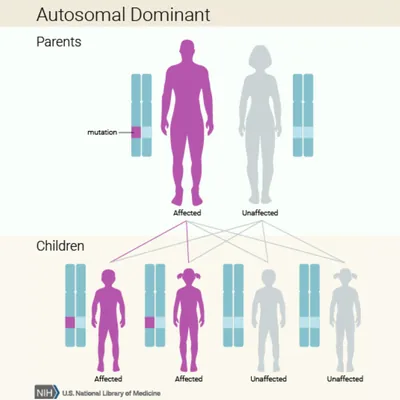
If you've visited your PCP, met with specialists, and undergone the recommended tests, but are still searching for a diagnosis, it may be time to visit an academic medical center or, for pediatric patients, a children's hospital. Academic medical centers and children's hospitals, often called multidisciplinary care centers, typically bring together specialists from different fields to work together on complex cases like rare diseases.
Multidisciplinary care centers may offer more coordinated care and be involved in clinical research, which may help reduce the time to diagnosis and provide access to emerging diagnostic tools. Specialists at these centers may have a deeper understanding of rare diseases and serve as a resource when you'd like a second opinion, particularly when test results or treatment plans are not delivering expected results.
Use this tool to find hospitals that may partner with medical schools and programs in your area.