Autosomal Dominant
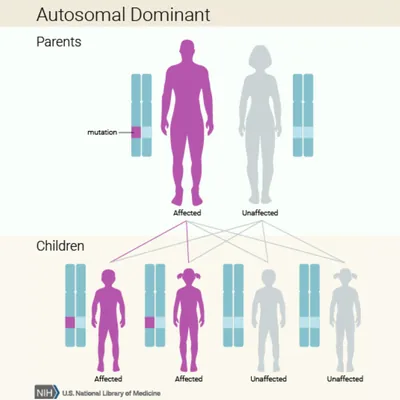
People affected by an autosomal dominant disease have a 50% chance of passing on the mutated gene to their biological child.
Learn more about inheritance patterns from the National Library of Medicine (NLM).
Many rare diseases have limited information. Currently, GARD aims to provide the following information for this disease:
23 Symptoms
GARD does not currently have information about the cause of this disease.
Yes. It is possible for a biological parent to pass down genetic mutations that cause or increase the chances of getting this disease to their child. This is known as inheritance. Knowing whether other family members have previously had this disease, also known as family health history, can be very important information for your medical team. This tool from the Surgeon General can help you collect your family health history.
There are multiple ways, or patterns, a disease can be inherited depending on the gene(s) involved. Based on GARD's current data, this disease can be inherited in the following pattern(s):

Patient organizations can help patients and families connect. They build public awareness of the disease and are a driving force behind research to improve patients' lives. They may offer online and in-person resources to help people live well with their disease. Many collaborate with medical experts and researchers.
Services of patient organizations differ, but may include:


9 Organizations
Organization Name
Who They Serve
Helpful Links
Country
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
United States
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
United Kingdom
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
United States
Clinical studies are part of clinical research and play an important role in medical advances, including for rare diseases. Through clinical studies, researchers may ultimately uncover better ways to treat, prevent, diagnose, and understand human diseases.

Clinical studies are medical research involving people as participants. There are two main types of clinical studies:
People participate in clinical trials for many reasons. People with a disease may participate to receive the newest possible treatment and additional care from clinical study staff as well as to help others living with the same or similar disease. Healthy volunteers may participate to help others and to contribute to moving science forward.
To find the right clinical study we recommend you consult your doctors, other trusted medical professionals, and patient organizations. Additionally, you can use ClinicalTrials.gov to search for clinical studies by disease, terms, or location.
ResearchMatch helps connect people interested in research studies with researchers from top medical centers across the United States. Anyone from the U.S. can register with this free program funded by NIH. Researchers from participating institutions use the database to search for and invite patients or healthy volunteers who meet their study criteria to participate.
The All of Us Research Program is inviting 1 million people from all backgrounds across the U.S. to help build one of the most diverse health databases in history. Researchers will use the data to learn how our biology, lifestyle, and environment affect health. This may one day help them find ways to treat and prevent diseases.
ResearchMatch helps connect people interested in research studies with researchers from top medical centers across the United States. Anyone from the U.S. can register with this free program funded by NIH. Researchers from participating institutions use the database to search for and invite patients or healthy volunteers who meet their study criteria to participate.
The All of Us Research Program is inviting 1 million people from all backgrounds across the U.S. to help build one of the most diverse health databases in history. Researchers will use the data to learn how our biology, lifestyle, and environment affect health. This may one day help them find ways to treat and prevent diseases.
Take steps toward getting a diagnosis by working with your doctor, finding the right specialists, and coordinating medical care.
Last Updated: February 2024