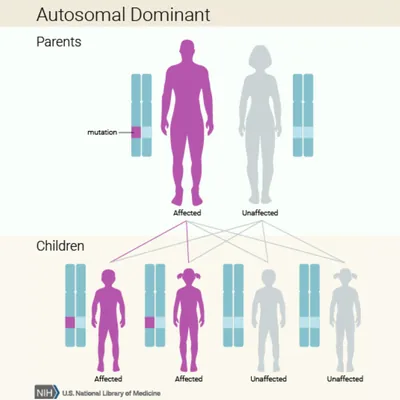
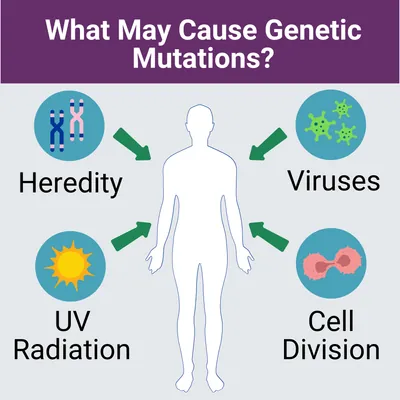
Genetic Mutations
If you suspect you may have this disease, you may want to start collecting your family health history. Information such as other family members who have had similar symptoms, when their/your symptoms first appeared, or exposures to any potential disease-causing environmental factors should be discussed with your medical team. This tool from the Surgeon General can help you collect your family health history.